集成到现有原生应用
如果你正准备从头开始制作一个新的应用,那么 React Native 会是个非常好的选择。但如果你只想给现有的原生应用中添加一两个视图或是业务流程,React Native 也同样不在话下。只需简单几步,你就可以给原有应用加上新的基于 React Native 的特性、画面和视图等。
具体的步骤根据你所开发的目标平台不同而不同。
译注:本文档可能更新不够及时,不能保证适用于最新版本,欢迎了解的朋友使用页面底部的编辑链接帮忙改进此文档。一个实用的建议是可以使用
npx react-native init NewProject创建一个最新版本的纯 RN 项目,去参考其 Podfile 或是 gradle 等的配置,以它们为准。
- Android (Java)
- iOS (Objective-C)
- iOS (Swift)
核心概念
把 React Native 组件集成到 Android 应用中有如下几个主要步骤:
- 配置好 React Native 依赖和项目结构。
- 创建 js 文件,编写 React Native 组件的 js 代码。
- 在应用中添加一个
ReactRootView。这个ReactRootView正是用来承载你的 React Native 组件的容器。 - 启动 React Native 的 Metro 服务,运行应用。
- 验证这部分组件是否正常工作。
开发环境准备
首先按照开发环境搭建教程来安装 React Native 在 Android 平台上所需的一切依赖软件。
1. 配置项目目录结构
首先创建一个空目录用于存放 React Native 项目,然后在其中创建一个/android子目录,把你现有的 Android 项目拷贝到/android子目录中。
2. 安装 JavaScript 依赖包
在项目根目录下创建一个名为package.json的空文本文件,然后填入以下内容:
{
"name": "MyReactNativeApp",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "yarn react-native start"
}
}
示例中的
version字段没有太大意义(除非你要把你的项目发布到 npm 仓库)。scripts中是用于启动 Metro 服务的命令。
接下来我们使用 yarn 或 npm(两者都是 node 的包管理器)来安装 React 和 React Native 模块。请打开一个终端/命令提示行,进入到项目目录中(即包含有 package.json 文件的目录),然后运行下列命令来安装:
$ yarn add react-native
这样默认会安装最新版本的 React Native,同时会打印出类似下面的警告信息(你可能需要滚动屏幕才能注意到):
warning "react-native@0.52.2" has unmet peer dependency "react@16.2.0".
这是正常现象,意味着我们还需要安装指定版本的 React:
$ yarn add react@16.2.0
注意必须严格匹配警告信息中所列出的版本,高了或者低了都不可以。
如果你使用多个第三方依赖,可能这些第三方各自要求的 react 版本有所冲突,此时应优先满足
react-native所需要的react版本。其他第三方能用则用,不能用则只能考虑选择其他库。
所有 JavaScript 依赖模块都会被安装到项目根目录下的node_modules/目录中(这个目录我们原则上不复制、不移动、不修改、不上传,随用随装)。
把node_modules/目录记录到.gitignore文件中(即不上传到版本控制系统,只保留在本地)。
把 React Native 添加到你的应用中
配置 maven
在你的 app 中 build.gradle 文件中添加 React Native 和 JSC 引擎依赖:
dependencies {
implementation "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:27.1.1"
...
implementation "com.facebook.react:react-native:+" // From node_modules
implementation "org.webkit:android-jsc:+"
}
如果想要指定特定的 React Native 版本,可以用具体的版本号替换
+,当然前提是你从 npm 里下载的是这个版本。
在项目的 build.gradle 文件中为 React Native 和 JSC 引擎添加 maven 源的路径,必须写在 "allprojects" 代码块中
allprojects {
repositories {
maven {
// All of React Native (JS, Android binaries) is installed from npm
url "$rootDir/../node_modules/react-native/android"
}
maven {
// Android JSC is installed from npm
url("$rootDir/../node_modules/jsc-android/dist")
}
...
}
...
}
确保依赖路径的正确!以免在 Android Studio 运行 Gradle 同步构建时抛出 “Failed to resolve: com.facebook.react:react-native:0.x.x" 异常。
启用原生模块的自动链接
要使用自动链接的功能,我们必须将其应用于几个地方。首先,将以下内容添加到settings.gradle:
apply from: file("../node_modules/@react-native-community/cli-platform-android/native_modules.gradle"); applyNativeModulesSettingsGradle(settings)
接下来,在app/build.gradle的最底部添加以下内容:
apply from: file("../../node_modules/@react-native-community/cli-platform-android/native_modules.gradle"); applyNativeModulesAppBuildGradle(project)
配置权限
接着,在 AndroidManifest.xml 清单文件中声明网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
如果需要访问 DevSettingsActivity 界面(即开发者菜单),则还需要在 AndroidManifest.xml 中声明:
<activity android:name="com.facebook.react.devsupport.DevSettingsActivity" />
开发者菜单一般仅用于在开发时从 Packager 服务器刷新 JavaScript 代码,所以在正式发布时你可以去掉这一权限。
允许明文传输(http 接口) (API level 28+)
从 Android 9 (API level 28)开始,默认情况下明文传输(http 接口)是禁用的,只能访问 https 接口。这将阻止应用程序连接到Metro bundler。下面的更改允许调试版本中的明文通信。
1. 为 debug 版本启用 usesCleartextTraffic选项
在src/debug/AndroidManifest.xml中添加usesCleartextTraffic选项:
<!-- ... -->
<application
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true" tools:targetApi="28" >
<!-- ... -->
</application>
<!-- ... -->
如果希望在正式打包后也能继续访问 http 接口,则需要在src/main/AndroidManifest.xml中也添加这一选项。
要了解有关网络安全配置和明文通信策略的更多信息,请参阅此链接。
代码集成
现在我们将修改原生 Android 应用程序以集成 React Native。
React Native 组件
我们首先要写的是"High Score"(得分排行榜)的 JavaScript 端的代码。
1. 创建一个index.js文件
首先在项目根目录中创建一个空的index.js文件。(注意一些老的教程可能提到,在 0.49 版本之前是 index.android.js 文件)
index.js是 React Native 应用在 Android 上的入口文件。而且它是不可或缺的!它可以是个很简单的文件,简单到可以只包含一行require/import导入语句。本教程中为了简单示范,把全部的代码都写到了index.js里(当然实际开发中我们并不推荐这样做)。
2. 添加你自己的 React Native 代码
在index.js中添加你自己的组件。这里我们只是简单的添加一个<Text>组件,然后用一个带有样式的<View>组件把它包起来。
import React from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
Text,
View
} from 'react-native';
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.hello}>Hello, World</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
var styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center'
},
hello: {
fontSize: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10
}
});
AppRegistry.registerComponent(
'MyReactNativeApp',
() => HelloWorld
);
3. 配置权限以便开发中的红屏错误能正确显示
如果你的应用会运行在 Android 6.0(API level 23)或更高版本,请确保你在开发版本中有打开悬浮窗(overlay)权限。你可以在代码中使用Settings.canDrawOverlays(this);来检查。之所以需要这一权限,是因为我们会把开发中的报错显示在悬浮窗中(仅在开发阶段需要)。在 Android 6.0(API level 23)中用户需要手动同意授权。具体请求授权的做法是在onCreate()中添加如下代码。其中OVERLAY_PERMISSION_REQ_CODE是用于回传授权结果的字段。
private final int OVERLAY_PERMISSION_REQ_CODE = 1; // 任写一个值
...
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
if (!Settings.canDrawOverlays(this)) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION,
Uri.parse("package:" + getPackageName()));
startActivityForResult(intent, OVERLAY_PERMISSION_REQ_CODE);
}
}
最后,必须重写onActivityResult()方法(如下面的代码所示)来处理权限接受或拒绝情况以实现一致的用户体验。此外,为了集成使用 startActivityForResult 的原生模块,我们需要将结果传递给 ReactInstanceManager 实例的 onActivityResult 方法。
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
if (requestCode == OVERLAY_PERMISSION_REQ_CODE) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
if (!Settings.canDrawOverlays(this)) {
// SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission not granted
}
}
}
mReactInstanceManager.onActivityResult( this, requestCode, resultCode, data );
}
核心组件:ReactRootView
我们还需要添加一些原生代码来启动 React Native 的运行时环境并让它开始渲染。首先需要在一个Activity中创建一个ReactRootView对象,然后在这个对象之中启动 React Native 应用,并将它设为界面的主视图。
如果你要在安卓 5.0 以下的系统上运行,请用
com.android.support:appcompat包中的AppCompatActivity代替Activity。
public class MyReactActivity extends Activity implements DefaultHardwareBackBtnHandler {
private ReactRootView mReactRootView;
private ReactInstanceManager mReactInstanceManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
SoLoader.init(this, false);
mReactRootView = new ReactRootView(this);
List<ReactPackage> packages = new PackageList(getApplication()).getPackages();
// 有一些第三方可能不能自动链接,对于这些包我们可以用下面的方式手动添加进来:
// packages.add(new MyReactNativePackage());
// 同时需要手动把他们添加到`settings.gradle`和 `app/build.gradle`配置文件中。
mReactInstanceManager = ReactInstanceManager.builder()
.setApplication(getApplication())
.setCurrentActivity(this)
.setBundleAssetName("index.android.bundle")
.setJSMainModulePath("index")
.addPackages(packages)
.setUseDeveloperSupport(BuildConfig.DEBUG)
.setInitialLifecycleState(LifecycleState.RESUMED)
.build();
// 注意这里的MyReactNativeApp 必须对应"index.js"中的
// "AppRegistry.registerComponent()"的第一个参数
mReactRootView.startReactApplication(mReactInstanceManager, "MyReactNativeApp", null);
setContentView(mReactRootView);
}
@Override
public void invokeDefaultOnBackPressed() {
super.onBackPressed();
}
}
执行"Sync Project files with Gradle"操作。
如果你使用的是 Android Studio , 可以使用Alt + Enter快捷键来自动为 MyReactActivity 类补上缺失的 import 语句。注意BuildConfig应该是在你自己的包中自动生成,无需额外引入。千万不要从com.facebook...的包中引入!
我们需要把 MyReactActivity 的主题设定为 Theme.AppCompat.Light.NoActionBar ,因为里面有许多组件都使用了这一主题。
<activity
android:name=".MyReactActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.NoActionBar">
</activity>
一个
ReactInstanceManager可以在多个 activities 或 fragments 间共享。你将需要创建自己的ReactFragment或ReactActivity,并拥有一个保存ReactInstanceManager的单例持有者。当你需要ReactInstanceManager(例如,将ReactInstanceManager连接到这些 Activities 或 Fragments 的生命周期)时,请使用单例提供的那个。
下一步我们需要把一些 activity 的生命周期回调传递给ReactInstanceManager:
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
if (mReactInstanceManager != null) {
mReactInstanceManager.onHostPause(this);
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
if (mReactInstanceManager != null) {
mReactInstanceManager.onHostResume(this, this);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (mReactInstanceManager != null) {
mReactInstanceManager.onHostDestroy(this);
}
if (mReactRootView != null) {
mReactRootView.unmountReactApplication();
}
}
我们还需要把后退按钮事件传递给 React Native:
@Override
public void onBackPressed() {
if (mReactInstanceManager != null) {
mReactInstanceManager.onBackPressed();
} else {
super.onBackPressed();
}
}
这允许JavaScript控制用户按下设备后退按钮时发生的情况(例如,执行导航时)。当JavaScript不处理后退按钮按下的情况时,将调用invokeDefaultOnBackPressed方法。默认情况下,这将完成你的Activity。
最后,我们需要连接开发菜单。默认情况下通过(狂)摇晃设备来激活,但这在模拟器中不是很有用,只有当你按下设备菜单按钮时才显示(如果你使用的是 Android Studio 模拟器,请使用Ctrl + M):
@Override
public boolean onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_MENU && mReactInstanceManager != null) {
mReactInstanceManager.showDevOptionsDialog();
return true;
}
return super.onKeyUp(keyCode, event);
}
现在 activity 已就绪,可以运行一些 JavaScript 代码了。
测试集成结果
你已经完成了将 React Native 与当前应用程序集成的所有基本步骤。现在我们将启动Metro bundler来构建index.bundle包,并通过本地主机提供服务。
1. 运行 Metro 服务
运行应用首先需要启动开发服务器(Metro)。你只需在项目根目录中执行以下命令即可:
$ yarn start
2. 运行你的应用
保持 Metro 的窗口运行不要关闭,然后像往常一样编译运行你的 Android 应用(在命令行中执行./gradlew installDebug或是在 Android Studio 中编译运行)。
编译执行一切顺利进行之后,在进入到 MyReactActivity 时应该就能立刻从 Metro 中读取 JavaScript 代码并执行和显示:
在 Android Studio 中打包
你也可以使用 Android Studio 来打 release 包!其步骤基本和原生应用一样,只是在每次编译打包之前需要先执行 js 文件的打包(即生成离线的 jsbundle 文件)。具体的 js 打包命令如下:
$ npx react-native bundle --platform android --dev false --entry-file index.js --bundle-output android/com/your-company-name/app-package-name/src/main/assets/index.android.bundle --assets-dest android/com/your-company-name/app-package-name/src/main/res/
注意把上述命令中的路径替换为你实际项目的路径。如果 assets 目录不存在,则需要提前自己创建一个。
然后在 Android Studio 中正常生成 release 版本即可!
然后呢?
然后就可以开发啦~可是我完全不会 React Native 怎么办?
我们建议你先通读本站的所有文档,看看博客,看看论坛。如果觉得知识太零散,不够系统,那么你也可以考虑下购买我们的付费咨询服务。
核心概念
把 React Native 组件集成到 iOS 应用中有如下几个主要步骤:
- 配置好 React Native 依赖和项目结构。
- 了解你要集成的 React Native 组件。
- 使用 CocoaPods 把这些组件以依赖的形式加入到项目中。
- 创建 js 文件,编写 React Native 组件的 js 代码。
- 在应用中添加一个
RCTRootView。这个RCTRootView正是用来承载你的 React Native 组件的容器。 - 启动 React Native 的 Packager 服务,运行应用。
- 验证这部分组件是否正常工作。
开发环境准备
首先按照开发环境搭建教程来安装 React Native 在 iOS 平台上所需的一切依赖软件。
1. 配置项目目录结构
首先创建一个空目录用于存放 React Native 项目,然后在其中创建一个/ios子目录,把你现有的 iOS 项目拷贝到/ios子目录中。
2. 安装 JavaScript 依赖包
在项目根目录下创建一个名为package.json的空文本文件,然后填入以下内容:
{
"name": "MyReactNativeApp",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "yarn react-native start"
}
}
示例中的
version字段没有太大意义(除非你要把你的项目发布到 npm 仓库)。scripts中是用于启动 Metro 服务的命令。
接下来我们使用 yarn 或 npm(两者都是 node 的包管理器)来安装 React 和 React Native 模块。请打开一个终端/命令提示行,进入到项目目录中(即包含有 package.json 文件的目录),然后运行下列命令来安装:
$ yarn add react-native
这样默认会安装最新版本的 React Native,同时会打印出类似下面的警告信息(你可能需要滚动屏幕才能注意到):
warning "react-native@0.52.2" has unmet peer dependency "react@16.2.0".
这是正常现象,意味着我们还需要安装指定版本的 React:
$ yarn add react@16.2.0
注意必须严格匹配警告信息中所列出的版本,高了或者低了都不可以。
如果你使用多个第三方依赖,可能这些第三方各自要求的 react 版本有所冲突,此时应优先满足
react-native所需要的react版本。其他第三方能用则用,不能用则只能考虑选择其他库。
所有 JavaScript 依赖模块都会被安装到项目根目录下的node_modules/目录中(这个目录我们原则上不复制、不移动、不修改、不上传,随用随装)。
把node_modules/目录记录到.gitignore文件中(即不上传到版本控制系统,只保留在本地)。
3. 安装 CocoaPods
CocoaPods是针对 iOS 和 Mac 开发的包管理工具。我们用它来把 React Native 框架的代码下载下来并添加到你当前的项目中。
我们建议使用Homebrew来安装 CocoaPods。
$ brew install cocoapods
把 React Native 添加到你的应用中
在本教程中我们用于示范的 app是一个2048类型的游戏。下面是这个游戏还没有集成React Native 时的主界面:
配置 CocoaPods 的依赖
提示,此部分说明可能落后于最新版本。建议使用
npx react-native init NewProject创建一个最新版本的纯 RN 项目,去参考其 Podfile 的配置。
React Native 框架整体是作为 node 模块安装到项目中的。下一步我们需要在 CocoaPods 的Podfile中指定我们所需要使用的"subspecs"。
可用的subspec都列在node_modules/react-native/React.podspec中,基本都是按其功能命名的。一般来说你首先需要添加Core,这一subspec包含了必须的AppRegistry、StyleSheet、View以及其他的一些 React Native 核心库。如果你想使用 React Native 的Text库(即<Text>组件),那就需要添加RCTText的subspec。同理,Image需要加入RCTImage,等等。
我们需要在Podfile文件中指定所需的subspec。创建Podfile的最简单的方式就是在/ios子目录中使用 CocoaPods 的init命令:
$ pod init
Podfile会创建在执行命令的目录中。你需要调整其内容以满足你的集成需求。调整后的Podfile的内容看起来类似下面这样(也可以用npx react-native init 项目名命令创建一个纯 RN 项目,然后去参考其 ios 目录中的 Podfile 文件):
# target的名字一般与你的项目名字相
# 'node_modules'目录一般位于根目录中
# 但是如果你的结构不同,那你就要根据实际路径修改下面的`:path`
pod 'FBLazyVector', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/FBLazyVector"
pod 'FBReactNativeSpec', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/FBReactNativeSpec"
pod 'RCTRequired', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/RCTRequired"
pod 'RCTTypeSafety', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/TypeSafety"
pod 'React', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/'
pod 'React-Core', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/'
pod 'React-CoreModules', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/React/CoreModules'
pod 'React-Core/DevSupport', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/'
pod 'React-RCTActionSheet', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/ActionSheetIOS'
pod 'React-RCTAnimation', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/NativeAnimation'
pod 'React-RCTBlob', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Blob'
pod 'React-RCTImage', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Image'
pod 'React-RCTLinking', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/LinkingIOS'
pod 'React-RCTNetwork', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Network'
pod 'React-RCTSettings', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Settings'
pod 'React-RCTText', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Text'
pod 'React-RCTVibration', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Vibration'
pod 'React-Core/RCTWebSocket', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/'
pod 'React-cxxreact', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/cxxreact'
pod 'React-jsi', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/jsi'
pod 'React-jsiexecutor', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/jsiexecutor'
pod 'React-jsinspector', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/jsinspector'
pod 'ReactCommon/callinvoker', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon"
pod 'ReactCommon/turbomodule/core', :path => "../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon"
pod 'Yoga', :path => '../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/yoga'
pod 'DoubleConversion', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/DoubleConversion.podspec'
pod 'glog', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/glog.podspec'
pod 'Folly', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/Folly.podspec'
end
创建好了Podfile后,就可以开始安装 React Native 的 pod 包了。
$ pod install
然后你应该可以看到类似下面的输出(译注:同样由于众所周知的网络原因,pod install 的过程在国内非常不顺利,请自行配备稳定的代理软件。)
Analyzing dependencies
Fetching podspec for `React` from `../node_modules/react-native`
Downloading dependencies
Installing React (0.62.0)
Generating Pods project
Integrating client project
Sending stats
Pod installation complete! There are 3 dependencies from the Podfile and 1 total pod installed.
If this fails with errors mentioning
xcrun, make sure that in Xcode in Preferences > Locations the Command Line Tools are assigned.
Mac M1 的注意事项
代码集成
现在我们已经准备好了所有依赖,可以开始着手修改原生代码来把 React Native 真正集成到应用中了。在我们的 2048 示例中,首先尝试添加一个显示有"High Score"(得分排行榜)的 React Native 页面。
React Native 组件
我们首先要写的是"High Score"(得分排行榜)的 JavaScript 端的代码。
1. Create a index.js file
首先在项目根目录下创建一个空的index.js文件。(注意在 0.49 版本之前是 index.ios.js 文件)
index.js是 React Native 应用在 iOS 上的入口文件。而且它是不可或缺的!它可以是个很简单的文件,简单到可以只包含一行require/import导入语句。本教程中为了简单示范,把全部的代码都写到了index.js里(当然实际开发中我们并不推荐这样做)。
2. 添加你自己的 React Native 代码
在index.js中添加你自己的组件。这里我们只是简单的添加一个<Text>组件,然后用一个带有样式的<View>组件把它包起来。
import React from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
Text,
View
} from 'react-native';
class RNHighScores extends React.Component {
render() {
var contents = this.props['scores'].map((score) => (
<Text key={score.name}>
{score.name}:{score.value}
{'\n'}
</Text>
));
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.highScoresTitle}>
2048 High Scores!
</Text>
<Text style={styles.scores}>{contents}</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF'
},
highScoresTitle: {
fontSize: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10
},
scores: {
textAlign: 'center',
color: '#333333',
marginBottom: 5
}
});
// Module name
AppRegistry.registerComponent('RNHighScores', () => RNHighScores);
RNHighScores是整体 js 模块(即你所有的 js 代码)的名称。你在 iOS 原生代码中添加 React Native 视图时会用到这个名称。
核心组件: RCTRootView
现在我们已经在index.js中创建了 React Native 组件,下一步就是把这个组件添加给一个新的或已有的ViewController。The easiest path to take is to optionally create an event path to your component and then add that component to an existing ViewController.
We will tie our React Native component with a new native view in the ViewController that will actually contain it called RCTRootView .
1. Create an Event Path
You can add a new link on the main game menu to go to the "High Score" React Native page.
2. 事件处理
现在我们将从菜单链接中添加一个事件处理程序。一个方法将被添加到你的应用程序的主ViewController中。这就是RCTRootView发挥作用的地方。
当你构建一个 React Native 应用时,需要使用 Metro(以前叫做 react packager)来创建一个index.bundle。index.bundle里面包含了我们的RNHighScore模块。因此,我们需要将RCTRootView指向index.bundle资源的位置(通过NSURL),并将其与模块绑定。
为了便于调试,我们将在事件处理程序被调用时输出日志。然后创建一个 URL 字符串,指向index.bundle的位置。最后,我们将创建主RCTRootView。请注意我们需要把上面创建的moduleName填进去,也就是RNHighScores。
首先导入RCTRootView的头文件。
#import <React/RCTRootView.h>
这里的
initialProperties注入了一些演示用的数据。在 React Native 的根组件中,我们可以使用this.props来获取到这些数据。
- (IBAction)highScoreButtonPressed:(id)sender {
NSLog(@"High Score Button Pressed");
NSURL *jsCodeLocation = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost:8081/index.bundle?platform=ios"];
RCTRootView *rootView =
[[RCTRootView alloc] initWithBundleURL: jsCodeLocation
moduleName: @"RNHighScores"
initialProperties:
@{
@"scores" : @[
@{
@"name" : @"Alex",
@"value": @"42"
},
@{
@"name" : @"Joel",
@"value": @"10"
}
]
}
launchOptions: nil];
UIViewController *vc = [[UIViewController alloc] init];
vc.view = rootView;
[self presentViewController:vc animated:YES completion:nil];
}
Note that
RCTRootView initWithURLstarts up a new JSC VM. To save resources and simplify the communication between RN views in different parts of your native app, you can have multiple views powered by React Native that are associated with a single JS runtime. To do that, instead of using[RCTRootView alloc] initWithURL, useRCTBridge initWithBundleURLto create a bridge and then useRCTRootView initWithBridge.
When moving your app to production, the
NSURLcan point to a pre-bundled file on disk via something like[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"main" withExtension:@"jsbundle"];. You can use thereact-native-xcode.shscript innode_modules/react-native/scripts/to generate that pre-bundled file.
3. Wire Up
Wire up the new link in the main menu to the newly added event handler method.
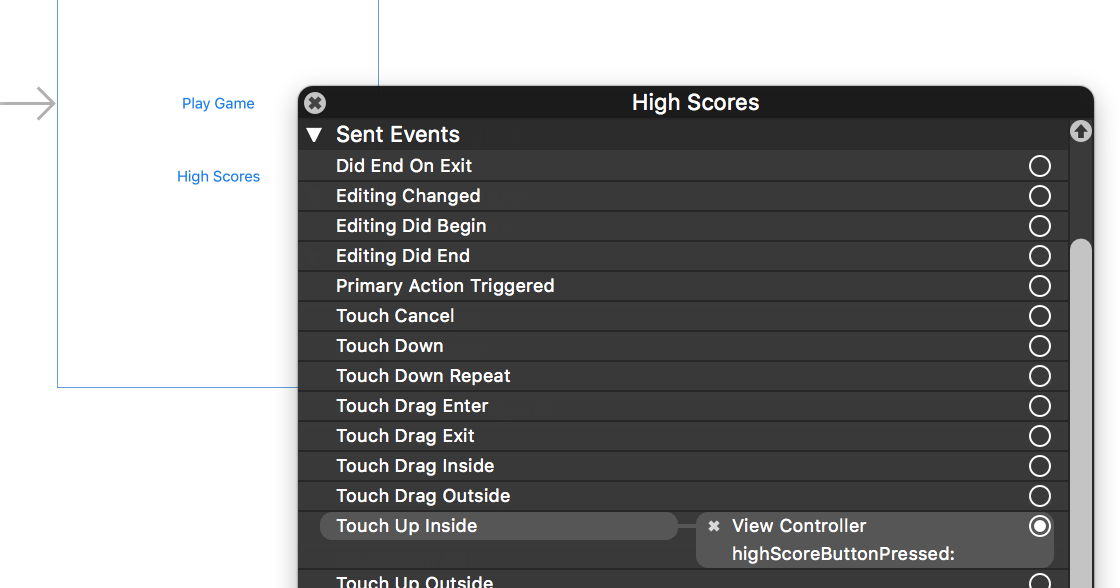
One of the easier ways to do this is to open the view in the storyboard and right click on the new link. Select something such as the
Touch Up Insideevent, drag that to the storyboard and then select the created method from the list provided.
测试集成结果
You have now done all the basic steps to integrate React Native with your current application. Now we will start the [Metro bundler][metro] to build the index.bundle package and the server running on localhost to serve it.
1. 添加 App Transport Security 例外
Apple 现在默认会阻止读取不安全的 HTTP 链接。所以我们需要把本地运行的 Metro 服务添加到Info.plist的例外中,以便能正常访问 Metro 服务:
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSExceptionDomains</key>
<dict>
<key>localhost</key>
<dict>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionAllowsInsecureHTTPLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
</dict>
</dict>
App Transport Security 对于用户来说是有利的。所以最好记得在发布之前重新启用这些安全限制。
2. 运行 Metro
要运行应用,首先需要启动开发服务器(即 Metro,它负责实时监测 js 文件的变动并实时打包,输出给客户端运行)。具体只需简单进入到项目根目录中,然后运行:
yarn start
3. 运行应用
如果你使用的是 Xcode,那么照常编译和运行应用即可。如果你没有使用 Xcode(但是你仍然必须安装 Xcode),则可以在命令行中使用以下命令来运行应用:
# 在项目的根目录中执行:
$ npx react-native run-ios
In our sample application, you should see the link to the "High Scores" and then when you click on that you will see the rendering of your React Native component.
Here is the native application home screen:
Here is the React Native high score screen:
If you are getting module resolution issues when running your application please see this GitHub issue for information and possible resolution. This comment seemed to be the latest possible resolution.
然后呢?
然后就可以开发啦~可是我完全不会 React Native 怎么办?
我们建议你先通读本站的所有文档,看看博客,看看论坛。如果觉得知识太零散,不够系统,那么你也可以考虑下购买我们的付费咨询服务。
核心概念
把 React Native 组件集成到 iOS 应用中有如下几个主要步骤:
- 配置好 React Native 依赖和项目结构。
- 了解你要集成的 React Native 组件。
- 使用 CocoaPods 把这些组件以依赖的形式加入到项目中。
- 创建 js 文件,编写 React Native 组件的 js 代码。
- 在应用中添加一个
RCTRootView。这个RCTRootView正是用来承载你的 React Native 组件的容器。 - 启动 React Native 的 Packager 服务,运行应用。
- 验证这部分组件是否正常工作。
开发环境准备
首先按照开发环境搭建教程来安装 React Native 在 iOS 平台上所需的一切依赖软件。
1. 配置项目目录结构
首先创建一个空目录用于存放 React Native 项目,然后在其中创建一个/ios子目录,把你现有的 iOS 项目拷贝到/ios子目录中。
2. 安装 JavaScript 依赖包
在项目根目录下创建一个名为package.json的空文本文件,然后填入以下内容:
{
"name": "MyReactNativeApp",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "yarn react-native start"
}
}
示例中的
version字段没有太大意义(除非你要把你的项目发布到 npm 仓库)。scripts中是用于启动 Metro 服务的命令。
接下来我们使用 yarn 或 npm(两者都是 node 的包管理器)来安装 React 和 React Native 模块。请打开一个终端/命令提示行,进入到项目目录中(即包含有 package.json 文件的目录),然后运行下列命令来安装:
$ yarn add react-native
这样默认会安装最新版本的 React Native,同时会打印出类似下面的警告信息(你可能需要滚动屏幕才能注意到):
warning "react-native@0.52.2" has unmet peer dependency "react@16.2.0".
这是正常现象,意味着我们还需要安装指定版本的 React:
$ yarn add react@16.2.0
注意必须严格匹配警告信息中所列出的版本,高了或者低了都不可以。
如果你使用多个第三方依赖,可能这些第三方各自要求的 react 版本有所冲突,此时应优先满足
react-native所需要的react版本。其他第三方能用则用,不能用则只能考虑选择其他库。
所有 JavaScript 依赖模块都会被安装到项目根目录下的node_modules/目录中(这个目录我们原则上不复制、不移动、不修改、不上传,随用随装)。
把node_modules/目录记录到.gitignore文件中(即不上传到版本控制系统,只保留在本地)。
3. 安装 CocoaPods
CocoaPods是针对 iOS 和 Mac 开发的包管理工具。我们用它来把 React Native 框架的代码下载下来并添加到你当前的项目中。
我们建议使用Homebrew来安装 CocoaPods。
$ brew install cocoapods
把 React Native 添加到你的应用中
在本教程中我们用于示范的 app是一个2048类型的游戏。下面是这个游戏还没有集成 React Native 时的主界面:
配置 CocoaPods 的依赖
提示,此部分说明可能落后于最新版本。建议使用
npx react-native init NewProject创建一个最新版本的纯 RN 项目,去参考其 Podfile 的配置。
React Native 框架整体是作为 node 模块安装到项目中的。下一步我们需要在 CocoaPods 的Podfile中指定我们所需要使用的"subspecs"。
可用的subspec都列在node_modules/react-native/React.podspec中,基本都是按其功能命名的。一般来说你首先需要添加Core,这一subspec包含了必须的AppRegistry、StyleSheet、View以及其他的一些 React Native 核心库。如果你想使用 React Native 的Text库(即<Text>组件),那就需要添加RCTText的subspec。同理,Image需要加入RCTImage,等等。
我们需要在Podfile文件中指定所需的subspec。创建Podfile的最简单的方式就是在/ios子目录中使用 CocoaPods 的init命令:
$ pod init
Podfile会创建在执行命令的目录中。你需要调整其内容以满足你的集成需求。调整后的Podfile的内容看起来类似下面这样(也可以用npx react-native init 项目名命令创建一个纯 RN 项目,然后去参考其 ios 目录中的 Podfile 文件):
source 'https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git'
# 对于Swift应用来说下面两句是必须的
platform :ios, '8.0'
use_frameworks!
# target的名字一般与你的项目名字相同
target 'swift-2048' do
# 'node_modules'目录一般位于根目录中
# 但是如果你的结构不同,那你就要根据实际路径修改下面的`:path
pod 'React', :path => '../node_modules/react-native', :subspecs => [
'Core',
'CxxBridge', # Include this for RN >= 0.47
'DevSupport', # Include this to enable In-App Devmenu if RN >= 0.43
'RCTText',
'RCTNetwork',
'RCTWebSocket', # needed for debugging
# Add any other subspecs you want to use in your project
]
# Explicitly include Yoga if you are using RN >= 0.42.0
pod "Yoga", :path => "../node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/yoga"
# Third party deps podspec link
pod 'DoubleConversion', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/DoubleConversion.podspec'
pod 'glog', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/glog.podspec'
pod 'Folly', :podspec => '../node_modules/react-native/third-party-podspecs/Folly.podspec'
end
创建好了Podfile后,就可以开始安装 React Native 的 pod 包了。
$ pod install
然后你应该可以看到类似下面的输出(译注:同样由于众所周知的网络原因,pod install 的过程在国内非常不顺利,请自行配备稳定的代理软件。)
Analyzing dependencies
Fetching podspec for `React` from `../node_modules/react-native`
Downloading dependencies
Installing React (0.62.0)
Generating Pods project
Integrating client project
Sending stats
Pod installation complete! There are 3 dependencies from the Podfile and 1 total pod installed.
If this fails with errors mentioning
xcrun, make sure that in Xcode in Preferences > Locations the Command Line Tools are assigned.
如果你看到类似"The
swift-2048 [Debug]target overrides theFRAMEWORK_SEARCH_PATHSbuild setting defined inPods/Target Support Files/Pods-swift-2048/Pods-swift-2048.debug.xcconfig. This can lead to problems with the CocoaPods installation"的警告,请查看 Xcode 的Build Settings中的Framework Search Paths选项,确保其中的Debug和Release都只包含$(inherited)。
Mac M1 的注意事项
代码集成
现在我们已经准备好了所有依赖,可以开始着手修改原生代码来把 React Native 真正集成到应用中了。在我们的 2048 示例中,首先尝试添加一个显示有"High Score"(得分排行榜)的 React Native 页面。
React Native 组件
我们首先要写的是"High Score"(得分排行榜)的 JavaScript 端的代码。
1. 创建一个index.js文件
首先在项目根目录下创建一个空的index.js文件。(注意在 0.49 版本之前是 index.ios.js 文件)
index.js是 React Native 应用在 iOS 上的入口文件。而且它是不可或缺的!它可以是个很简单的文件,简单到可以只包含一行require/import导入语句。本教程中为了简单示范,把全部的代码都写到了index.js里(当然实际开发中我们并不推荐这样做)。
2. 添加你自己的 React Native 代码
在index.js中添加你自己的组件。这里我们只是简单的添加一个<Text>组件,然后用一个带有样式的<View>组件把它包起来。
import React from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
Text,
View
} from 'react-native';
class RNHighScores extends React.Component {
render() {
var contents = this.props['scores'].map((score) => (
<Text key={score.name}>
{score.name}:{score.value}
{'\n'}
</Text>
));
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.highScoresTitle}>
2048 High Scores!
</Text>
<Text style={styles.scores}>{contents}</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF'
},
highScoresTitle: {
fontSize: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10
},
scores: {
textAlign: 'center',
color: '#333333',
marginBottom: 5
}
});
// 整体js模块的名称
AppRegistry.registerComponent('RNHighScores', () => RNHighScores);
RNHighScores是整体 js 模块(即你所有的 js 代码)的名称。你在 iOS 原生代码中添加 React Native 视图时会用到这个名称。
核心组件:RCTRootView
现在我们已经在index.js中创建了 React Native 组件,下一步就是把这个组件添加给一个新的或已有的ViewController。 The easiest path to take is to optionally create an event path to your component and then add that component to an existing ViewController.
We will tie our React Native component with a new native view in the ViewController that will actually contain it called RCTRootView .
1. Create an Event Path
You can add a new link on the main game menu to go to the "High Score" React Native page.
2. 事件处理
现在我们将从菜单链接中添加一个事件处理程序。一个方法将被添加到你的应用程序的主ViewController中。这就是RCTRootView发挥作用的地方。
当你构建一个 React Native 应用时,需要使用 Metro(以前叫做 react packager)来创建一个index.bundle。index.bundle里面包含了我们的RNHighScore模块。因此,我们需要将RCTRootView指向index.bundle资源的位置(通过NSURL),并将其与模块绑定。
为了便于调试,我们将在事件处理程序被调用时输出日志。然后创建一个 URL 字符串,指向index.bundle的位置。最后,我们将创建主RCTRootView。请注意我们需要把上面创建的moduleName填进去,也就是RNHighScores。
首先import导入React库。
import React
这里的
initialProperties注入了一些演示用的数据。在 React Native 的根组件中,我们可以使用this.props来获取到这些数据。
@IBAction func highScoreButtonTapped(sender : UIButton) {
NSLog("Hello")
let jsCodeLocation = URL(string: "http://localhost:8081/index.bundle?platform=ios")
let mockData:NSDictionary = ["scores":
[
["name":"Alex", "value":"42"],
["name":"Joel", "value":"10"]
]
]
let rootView = RCTRootView(
bundleURL: jsCodeLocation,
moduleName: "RNHighScores",
initialProperties: mockData as [NSObject : AnyObject],
launchOptions: nil
)
let vc = UIViewController()
vc.view = rootView
self.present(vc, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
Note that
RCTRootView bundleURLstarts up a new JSC VM. To save resources and simplify the communication between RN views in different parts of your native app, you can have multiple views powered by React Native that are associated with a single JS runtime. To do that, instead of usingRCTRootView bundleURL, useRCTBridge initWithBundleURLto create a bridge and then useRCTRootView initWithBridge.
When moving your app to production, the
NSURLcan point to a pre-bundled file on disk via something likelet mainBundle = NSBundle(URLForResource: "main" withExtension:"jsbundle"). You can use thereact-native-xcode.shscript innode_modules/react-native/scripts/to generate that pre-bundled file.
3. Wire Up
Wire up the new link in the main menu to the newly added event handler method.

One of the easier ways to do this is to open the view in the storyboard and right click on the new link. Select something such as the
Touch Up Insideevent, drag that to the storyboard and then select the created method from the list provided.
测试集成结果
You have now done all the basic steps to integrate React Native with your current application. Now we will start the [Metro bundler][metro] to build the index.bundle package and the server running on localhost to serve it.
1. 添加 App Transport Security 例外
Apple 现在默认会阻止读取不安全的 HTTP 链接。所以我们需要把本地运行的 Packager 服务添加到Info.plist的例外中,以便能正常访问 Packager 服务:
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSExceptionDomains</key>
<dict>
<key>localhost</key>
<dict>
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionAllowsInsecureHTTPLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
</dict>
</dict>
App Transport Security 对于用户来说是有利的。所以最好记得在发布之前重新启用这些安全限制。
2. 运行 Metro
要运行应用,首先需要启动开发服务器(即 Metro,它负责实时监测 js 文件的变动并实时打包,输出给客户端运行)。具体只需简单进入到项目根目录中,然后运行:
$ npm start
3. 运行应用
如果你使用的是 Xcode,那么照常编译和运行应用即可。如果你没有使用 Xcode(但是你仍然必须安装 Xcode),则可以在命令行中使用以下命令来运行应用:
# 在项目的根目录中执行:
$ npx react-native run-ios
In our sample application, you should see the link to the "High Scores" and then when you click on that you will see the rendering of your React Native component.
Here is the native application home screen:
Here is the React Native high score screen:
If you are getting module resolution issues when running your application please see this GitHub issue for information and possible resolution. This comment seemed to be the latest possible resolution.
然后呢?
然后就可以开发啦~可是我完全不会 React Native 怎么办?
我们建议你先通读本站的所有文档,看看博客,看看论坛。如果觉得知识太零散,不够系统,那么你也可以考虑下购买我们的付费咨询服务。